Model No: 124433-A12
- Best Quality
- Affordable Pricing
- On-Time Delivery
- Customer Satisfaction
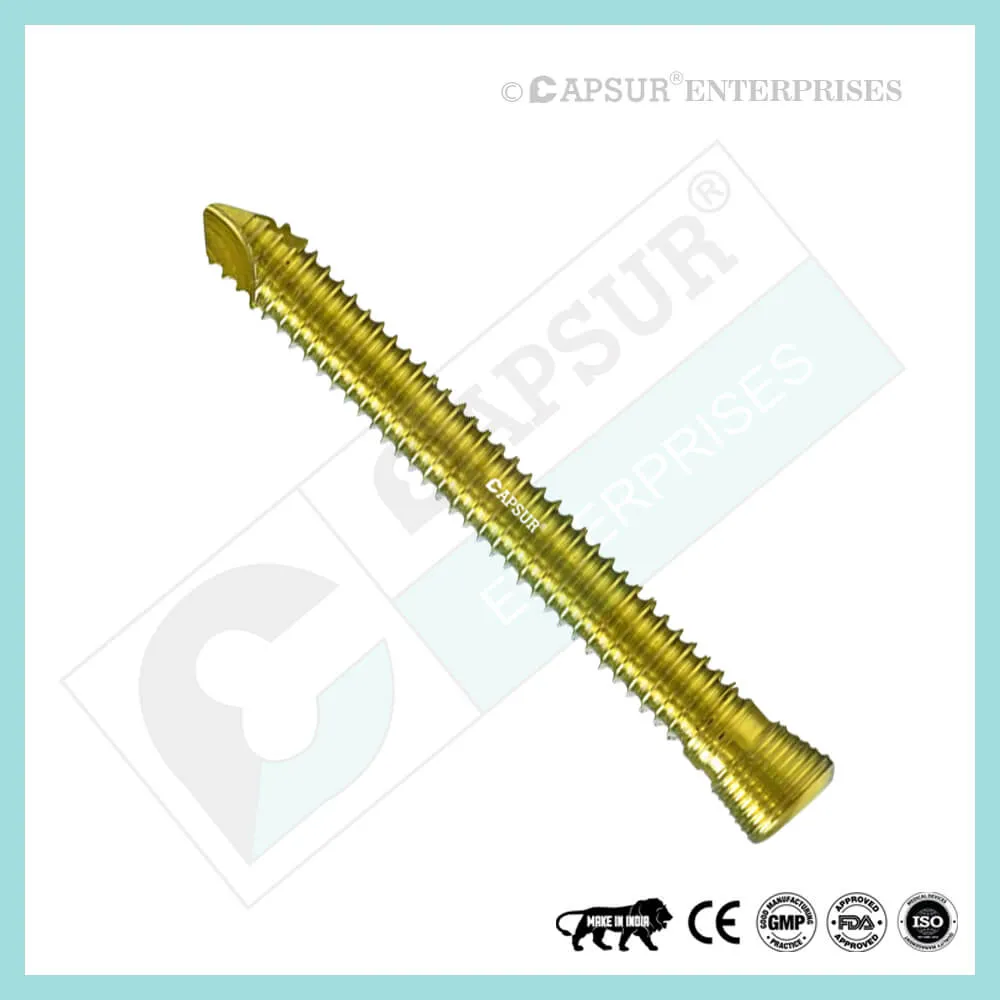
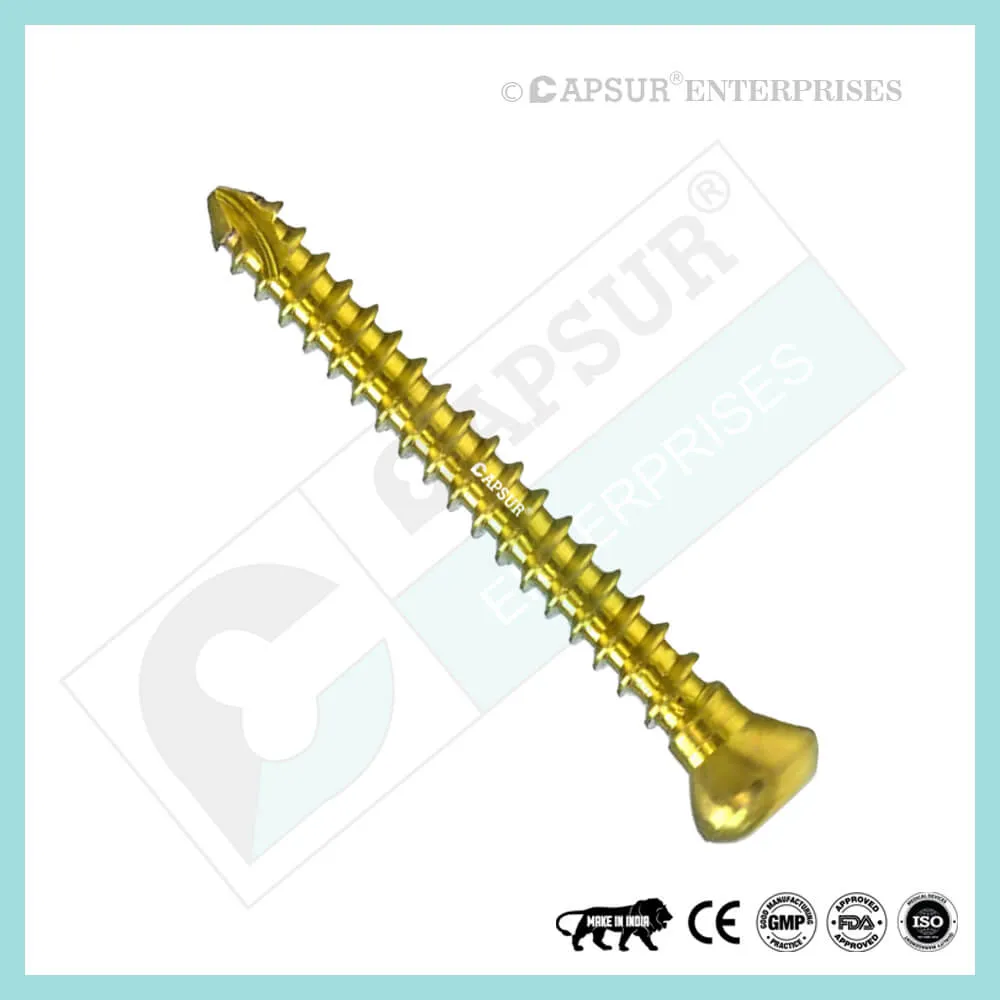
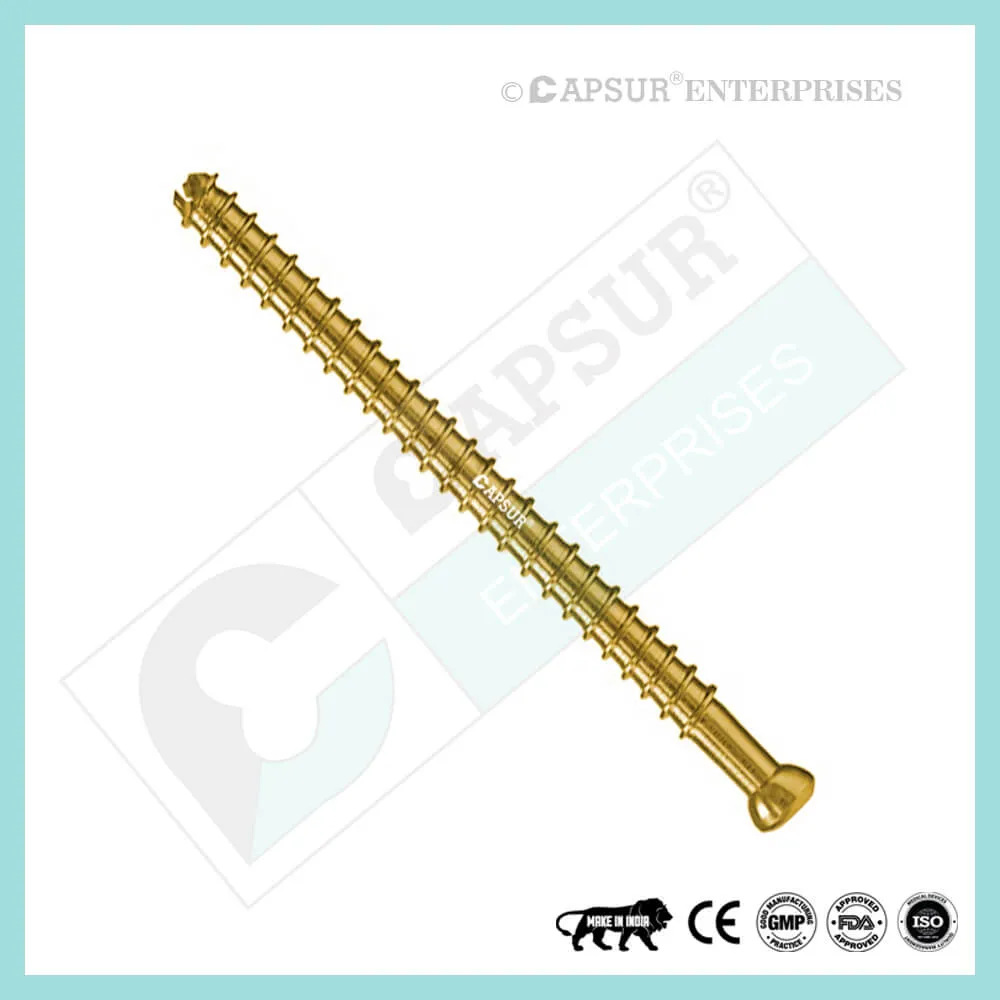
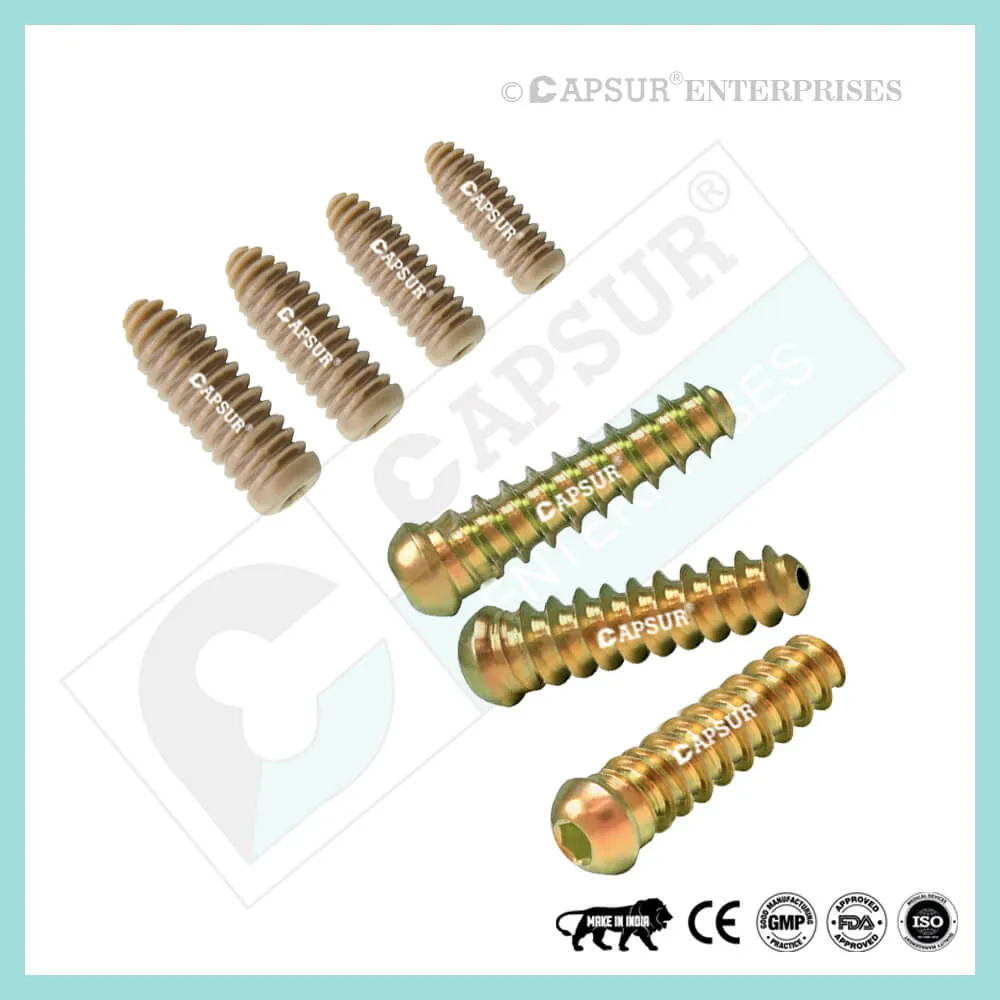
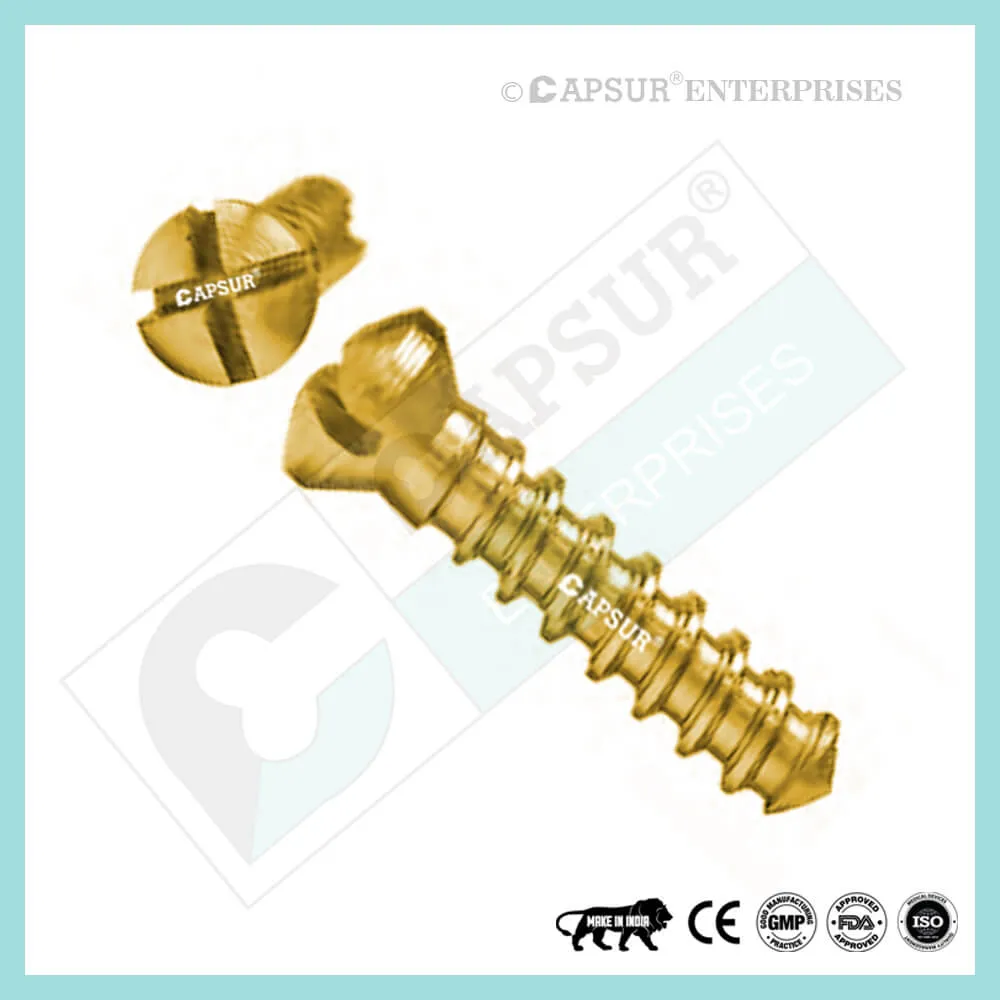
Specification for 5 mm Locking Cortical Screws
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw available lengths are 10mm, 12mm, 14mm, 16mm, 18mm, 20mm, 22mm, 24mm, 26mm, 28mm, 30mm, 32mm, 34mm, 36mm, 38mm, 40mm, 42mm, 44mm, 46mm, 48mm, 50mm, 52mm, 54mm, 56mm, 58mm, 60mm, 65mm, 70mm, 75mm, 80mm, 85mm, 90mm, 95mm, 100mm. 105mm, 110mm, 115mm and 120mm.
The 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw is constructed of 316L stainless steel and pure titanium.
This screw will be produced on demand in any additional length sizes.
Self-tapping screw, that is. Self-Tapping Screws create their own thread as they are inserted into the bone. When it enters the bone, it makes a tiny hole that results in a close friction fit between the threads. This prevents vibration-induced part loosening and enables the components to be disassembled if necessary.
For this screw, tools like bone taps, combined drill and tap sleeves, counter sinks, depth gauges, drill guides, drill sleeves, hollow mill screw removal tools, reverse measuring devices, screw drivers, and screw holding forceps are all available.
Uses of 5 mm Locking Cortical Screws
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw is used in fixation of 5 mm locking plates.
Other Useful Info of 5 mm Locking Cortical Screws
Different Types of Screws including 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw
Locking Cortical Screws
- 2 mm Locking Cortical Screws
- 2.4 mm Locking Cortical Screws
- 2.7 mm Locking Cortical Screws
- 3.5 mm Locking Cortical Screws
- 5 mm Locking Cortical Screws
Cortical Screws
- 1.5 mm Cortical Screws
- 2 mm Cortical Screws
- 2.4 mm Cortical Screws
- 2.7 mm Cortical Screws
- 3.5 mm Cortical Screws
- 4.5 mm Cortical Screws
Locking Cancellous Screws
- 3.5 mm Locking Cancellous Screw
- 4 mm Locking Cancellous Screw
- 5 mm Locking Cancellous Screw
- 6.5 mm Locking Cancellous Screw
Cancellous Screws
- 3.5 mm Cancellous Screw
- 4 mm Cancellous Screw
- 6.5 mm Cancellous Screw
Locking Cannulated Screws
- 4 mm Locking Cannulated Screw
- 5 mm Locking Cannulated Screw
- 6.5 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw
- 7.3 mm Locking Cannulated Cancellous Screw
Cannulated Screws
- 3.5 mm Cannulated Screws (Cortical Thread)
- 4 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screws
- 4.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screws
- 6.5 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screws
- 7 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screws
- 7.3 mm Cannulated Cancellous Screws
Headless Screws Full Thread
- 2.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 3 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 3.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 4 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 4.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 5.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
- 6.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Full Thread
Headless Screws Partially Thread
- 2.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 3 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 3.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 4 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 4.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 5.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 6.5 mm Headless Compression Screws Partially Thread
- 7.5 mm Headless Compression Screw Partially Thread
Interlocking Nail Screws
PFNA2 Blades
PFNA Blades
- 8 mm Proximal Cannulated Bolt
- 6.4 mm Proximal Cannulated Bolt
- 4.9 mm Locking Bolts
- 3.9 mm Locking Bolts
- 3.4 mm Locking Bolts
Interference Screws
- 5 mm Interference Screw
- 6 mm Interference Screw
- 7 mm Interference Screw
- 8 mm Interference Screw
- 9 mm Interference Screw
- 10 mm Interference Screw
Herbert Screws
- 2.5 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
- 3 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
- 3.5 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
- 4.5 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
- 5.5 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
- 6.5 mm Cannulated Herbert Screws
Craniomaxillofacial Screws
- 1.5 mm Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2 mm Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2 mm Locking Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2.5 mm Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2.5 mm Locking Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2.8 mm Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2.8 mm Locking Screw Craniomaxillofacial
- 2.7 mm Emergency Screw
Malleolar Screws
- 3.5 mm Malleolar Screws
- 4.5 mm Malleolar Screws
The most frequently used orthopedic implants are bone screws. For various types of bones, there are numerous types and sizes of screws. The majority of bone screws are constructed from titanium or stainless steel alloys. When determining screw mechanics, it’s important to consider the outer diameter, root diameter, thread pitch, and angle.
For example, a “5 mm Locking Cortical Screw” has an outside diameter of 5 mm. In orthopedics, screws are typically described by their outer diameter. The linear distance covered by a screw during one complete turn is known as the pitch of the screw. With each full turn, the screw moves forward by a distance equal to the space between the threads. Cortical screws have more threads because they have a lower pitch. Given the fragility of the bone, cancellous bone screws have a deeper screw to increase surface area and enhance purchase.
Screws work by converting the torque applied to tighten them into internal tension and elastic responses in the bone around them. The fracture fragments that the screw is holding together are compressed as a result. Typically, screws are inserted into holes that have been drilled to the same diameter as the root and are either self-tapping or have been tapped (threaded) beforehand. The screws must be properly inserted into the proper size drilled hole and made to withstand the insertion torque levels anticipated in cortical bone because the torque to insert cortical bone screws can be high. Large, deep threads on cancellous bone screws allow them to securely hold the spongy bone. It is uncommon for a screw to fail during insertion due to the cancellous bone’s relatively low strength, but pull out can be problematic.
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw Risk Factor
When assessing the prognosis in each case, contraindications—which may be partial or complete—must be taken into account. Under the following circumstances, alternative management strategies may need to be taken into account:
- infections that are systemic or local, acute or chronic.
- either localized, systemic, or chronic inflammation.
- serve as a dangerous vascular, nervous, or muscular disease.
- Bone defects that would prevent the implant from being properly anchored.
- All associated illnesses that might jeopardize the implant’s success and functionality.
Warnings and Precautionary for 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw
Before using the 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw, the surgeon and support personnel should read the safety instructions in this document as well as any product-specific information in the product description, surgical techniques, and/or brochures.
Screws are carefully designed, built, and produced using materials of the highest quality for medical use. If used properly, these high-quality screws guarantee the best working outcomes. The usage guidelines and safety advice that are provided below must be followed.
Incorrect screw usage can result in tissue damage, premature wear, instrument destruction, injury to the operator, patients, or other people, and injury to the tissue.
It is essential that the operating surgeon actively participate in the medical care of their patients. All facets of the surgical procedure and the tools used, including their limitations, should be fully understood by the surgeon. It is the surgeon’s and the surgical team’s responsibility to take care in the selection and use of surgical instruments. Prior to using implants, sufficient surgical training must be obtained.
The following variables could harm the operation’s success:
- implanted material allergies.
- specific bone tumors.
- both osteoporosis and osteomalacia.
- disordered metabolism and systemic disease.
- abuse of drugs and alcohol.
- The implant is exposed to blows and/or excessive loading during physical activities that involve strong shocks.
- Patients who are mentally incapable of understanding and following instructions from the doctor.
- unhealthy in general.
- Effects that could be harmful
The most frequent side effects of implantation are the ones listed below:
- cyclic loading of the fixation site and/or an implant’s response to tissue can both lead to screw loosening.
- infection both early and late.
- additional bone fracture brought on by unusual stress or weakening of the bone matrix.
- pressure or hematoma-induced temporary or permanent neural damage.
- Hemorrhages and slow wound healing.
- Heart arrest, pulmonary embolism, and venal thrombosis are examples of vascular disease.
- Ossification that is heterotopic.
- due to the 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw’s presence, discomfort and pain.
- Failure due to mechanical forces, such as bending, loosening, or breakage of the implant.
- Implant migration that causes harm.
Preoperative Planning for 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw
A thorough clinical evaluation of the patient is followed by the execution of the operating plan. X-rays are also required to provide a clear picture of the bony anatomy and any associated deformities. In addition to a full size 5 mm Locking Cortical Screw, the appropriate implantation tools must be on hand at the time of the procedure.
The patient should be informed of any potential risks and side effects related to implant use by the clinician. It is critical to ascertain the patient’s allergy status to all implant materials prior to surgery. The patient must also be made aware that the device’s performance cannot be guaranteed because problems may shorten the device’s useful life.
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw Precautions
During reprocessing, verify that the instruments are functional and look for wear. Before using, replace any worn-out or broken instruments.
It is advised to use the tools designated for this screw.
Use caution when handling equipment, and put used bone-cutting tools in a sharps container.
Always use suction and irrigation to remove any debris that may be produced during implantation or removal.
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw Warnings
Locking 5 mm Cortical During use, a screw may break (if excessive forces are applied). We advise that the broken part be removed whenever possible and practical for the particular patient, though the surgeon will ultimately decide whether to do so based on the risk involved. Be aware that implants lack the natural bone’s strength. Significant loads may cause implants to fail.
The user’s glove or skin may be pinched or torn by the sharp edges or moving joints of some instruments, screws, and cut plates.
Be sure to get rid of any fragments that weren’t fixed during surgery.
While the surgeon will ultimately decide whether to remove the implant, we advise that fixation devices be taken out as soon as it is safe and practical for the specific patient and after their purpose as a healing aid has been fulfilled. To prevent refracture, implant removal should be followed by adequate post-operative care.
5 mm Locking Cortical Screw General Adverse Events
There are risks, side effects, and adverse events associated with all major surgical procedures. While there are many possible reactions, the following are some of the most frequent ones: issues related to anesthesia and patient positioning (such as nausea, vomiting, dental injuries, neurological impairments, etc.), thrombosis, embolism, infection, damage to nerve and/or tooth roots or other critical structures, such as blood vessels, excessive bleeding, damage to soft tissues, including swelling, abnormal scar formation, functional impairment of the musculoskeletal system, and pain.
| 5 mm Locking Cortical Screws |
|---|