Model No: 124433-A12
- Best Quality
- Affordable Pricing
- On-Time Delivery
- Customer Satisfaction
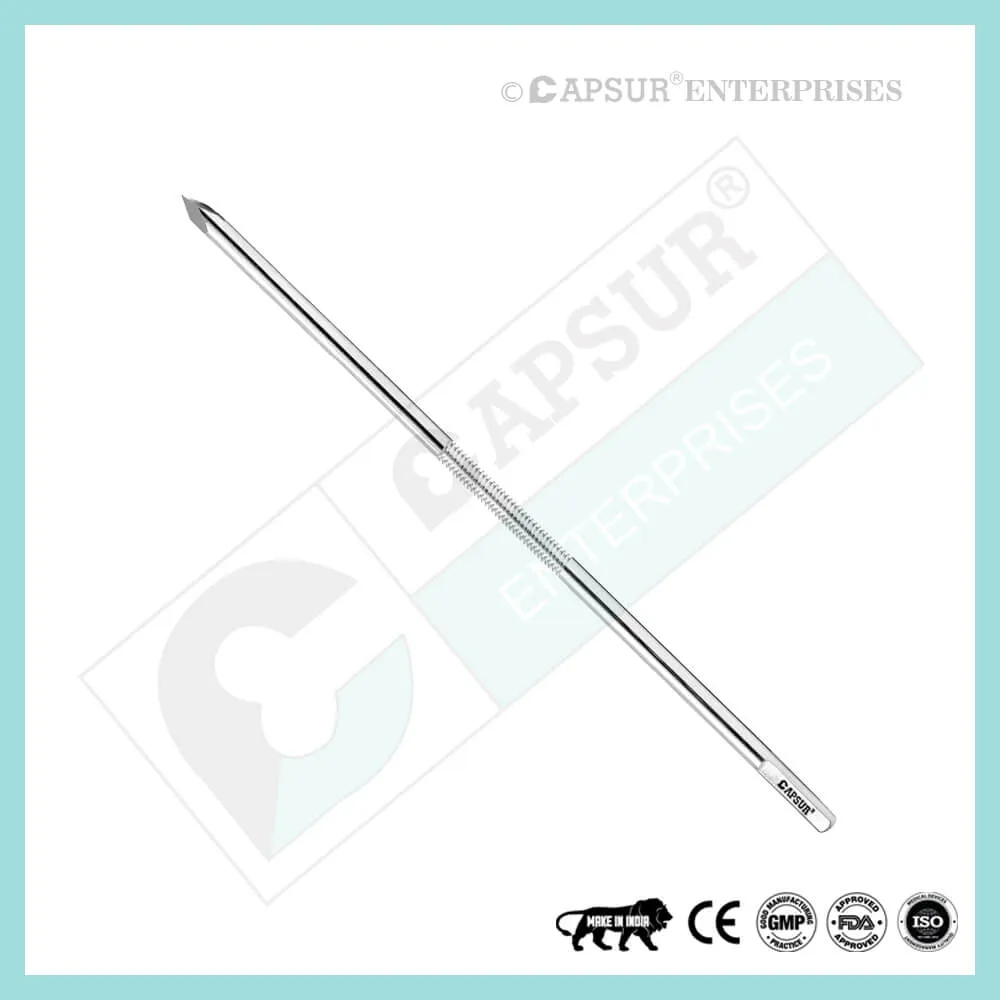
Specification of Schanz Screw (Schanz Pin) Self Tapping
- Schanz Pins are metal rods that have one end with pointed threads and the other end shaped to fit into an attachment mechanism.
- There are many types, lengths, and diameters of Schanz pins.
- Tapered threaded, self-tapping, and self-drilling types
- Dimensions: 4, 4.5, 5, 5.5, 6, and 6.5 mm
- 60 mm to 300 mm in length
- For the purpose of minimizing complications related to pin-tracts in external fixation, Schanz Pin Self Drilling was created to optimize the bone/pin interface.
- Schanz Pin Self Drilling’s innovative design improves pullout resistance in cortical and cancellous bone while lowering heat generation and insertion torque.
Uses of Schanz Screw (Schanz Pin) Self Tapping
For open or closed fracture fixation, pseudoarthrosis or nonunion of long bones, limb lengthening by epiphyseal or metaphyseal distraction, correction of bony or soft tissue deformity, correction of segmental bony or soft tissue deformity, correction of segmental bony or soft tissue defects, and joint arthrodesis are all conditions for which the Schanz Pin is intended to be used with an external fixation system.
Other Important Info of Schanz Screw (Schanz Pin) Self Tapping
Schanz Pin Self Tapping
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 20 x 80 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 30 x 100 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 125 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 150 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4 x 40 x 175 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 20 x 60 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 20 x 80 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 30 x 100 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 125 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 150 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5 x 40 x 175 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 30 x 100 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 40 x 125 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 60 x 150 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 60 x 175 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 80 x 200 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.0 x 80 x 250 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 30 x 100 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 40 x 125 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 60 x 150 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 60 x 175 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 80 x 200 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 5.5 x 80 x 250 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 30 x 100 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 40 x 125 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 60 x 150 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 60 x 175 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 80 x 200 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6 x 80 x 250 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 200 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 225 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 80 x 250 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 90 x 275 mm
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6.5 x 100 x 300 mm
Schanz Pin Tapered Threaded Sizes
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 20 x 80
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 20 x 100
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 100
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 120
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 30 x 140
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 120
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 140
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 4.5-3.5 x 40 x 160
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 100
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 120
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 140
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 30 x 160
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 140
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 160
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 180
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 40 x 200
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 160
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 180
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 200
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 50 x 220
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 180
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 200
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 220
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 60 x 240
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 200
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 220
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 70 x 240
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 80 x 220
- Dia x Thread Length x Total Length = 6-5 x 80 x 250
Preoperative Planning for Schanz Pins
- surgical technique using a Schanz pin on the tibia
- Anteromedial to the tibia is the soft tissue region where Schanz Pins can be inserted without endangering crucial structures (vessels, nerves, muscles, and tendons). This safe area has a variety of angles.
- The anterior tibial artery damage can be prevented by avoiding the lateral surface of the distal third of the tibia.
- Interference with the tendons can also be prevented if the ventral zone of the distal tibia is avoided.
- surgical technique using a Schanz pin on the femur
- It is advised to approach the femur from the side at a 30° angle. It is also possible to approach medially from a distal angle.
- surgical technique using the Schanz Pin for the pelvis
- The external fixation assembly’s pin placement in the pelvis comes in two recommended configurations.
Supraacetabular pin placement
The more technically challenging supraacetabular pin placement is preferred over that of the iliac crest due to the prominent bone structure. The site of entry is roughly 4-6 cm in a caudal direction and 3-4 cm in a medial direction, starting from the superior anterior crest.
The alignment for drilling the Pins when the patient is supine is angled roughly 20° in a cranial direction and 30° inward.
Location of the iliac crest pin
Precaution: Avoid insertion up to 15 mm dorsally from the superior anterior iliac spine to prevent injury to the femoral cutaneous nerve.
Palpating the os ilium with a finger or another instrument will reveal its orientation. The pins are then carefully inserted between the os ilium’s two laminae.
Surgical Preparation for Schanz Pins Plevis
Schanz Pin approach to the humerus
A dorsal approach to the humerus is suitable from a distance.
Precautions: The radial and axillary nerves should be given priority when working with the humerus. A dorsal approach to the humerus is suitable from a distance. In close proximity, it is advised to insert the Schanz Pins ventrolaterally, caudal to the course of the axillary nerve.
Technique for the placement of Schanz Pin into bone using minimal radiologic control
In both elective and trauma orthopaedic surgery, Schanz Pin is typically inserted into the bone during external-fixation procedures under röentgenologic supervision. We outline an easy method of placing Schanz Pins in order to reduce radiation exposure for both patients and surgeons. Only at the start and end of the procedure is the position of the half-pins subject to röentgenologic control. The operation will take less time with this straightforward method, and both the patient and the surgeon will receive less radiation exposure. It is a helpful technique in many resource-poor environments that lack the infrastructure for an image intensifier fluoroscopy or C-arm as well as in harsh conditions like those that arise during military operations.
Schanz Pin Risk Factor
When assessing the prognosis in each case, contraindications—which may be partial or complete must be taken into account. Under the following circumstances, alternative management strategies may need to be taken into account:
- infections that are systemic or local, acute or chronic.
- either localized, systemic, or chronic inflammation.
- serve as a dangerous vascular, nervous, or muscular disease.
- Bone defects that would prevent the implant from being properly anchored.
- All associated illnesses that might jeopardize the implant’s success and functionality.
Warnings and Precautionary for Schanz Pin
Before using Schanz Pin, the surgeon and supporting personnel should read the safety instructions as well as any product-specific information in the product description, surgical techniques, and/or brochures.
The materials used to make the pin are of the highest quality and were carefully planned, built, and produced. As long as they are used correctly, these high-quality pins guarantee the best working outcomes. The usage guidelines and safety advice that are provided below must be followed.
Improper use of a pin can cause injury to the operator, patients, or other people in addition to causing tissue damage, premature wear, instrument destruction, and injury.
It is essential that the operating surgeon actively participate in the medical care of their patients. All facets of the surgical procedure and the tools used, including their limitations, should be fully understood by the surgeon. It is the surgeon’s and the surgical team’s responsibility to take care in the selection and use of surgical instruments. Prior to using implants, sufficient surgical training must be obtained.
The following variables could harm the operation’s success:
- implanted material allergies.
- specific bone tumors.
- both osteoporosis and osteomalacia.
- disordered metabolism and systemic disease.
- abuse of drugs and alcohol.
- The implant is exposed to blows and/or excessive loading during physical activities that involve strong shocks.
- Patients who are mentally incapable of understanding and following instructions from the doctor.
- unhealthy in general.
- Effects that could be harmful
- The most frequent side effects of implantation are the ones listed below:
- A tissue reaction to the implant or cyclic loading of the fixation site may cause the pin to loosen.
- infection both early and late.
- additional bone fracture brought on by unusual stress or weakening of the bone matrix.
- pressure or hematoma-induced temporary or permanent neural damage.
- Hemorrhages and slow wound healing.
- Heart arrest, pulmonary embolism, and venal thrombosis are examples of vascular disease.
- Ossification that is heterotopic.
- Pain and discomfort brought on by the Schanz Pin’s presence.
- Failure due to mechanical forces, such as bending, loosening, or breakage of the implant.
- Implant migration that causes harm.
Preoperative Planning for Schanz Pin
Following a thorough clinical evaluation of the patient, the operation is planned. X-rays are also necessary to provide a clear picture of the bony anatomy and any associated deformities. Along with a full size Schanz Pin, the appropriate implantation tools must be on hand at the time of the procedure.
The potential risks and complications related to the use of implants should be discussed with the patient by the clinician. If the patient has allergies to any of the implant materials, it is crucial to know this before surgery. Additionally, the patient needs to be made aware that the device’s performance cannot be guaranteed because problems may reduce its lifespan.
Schanz Pin Precautions
During reprocessing, verify that the instruments are functional and look for wear. Before using, replace any worn-out or broken instruments.
Utilizing the tools designated for this Pin is advised.
Use caution when handling equipment, and put used bone-cutting tools in a sharps container.
Always use suction and irrigation to remove any debris that may be produced during implantation or removal.
Schanz Pin Warnings
Schanz During use, a pin may break (if excessive forces are applied). We advise that the broken part be removed whenever possible and practical for the particular patient, though the surgeon will ultimately decide whether to do so based on the risk involved. Be aware that implants lack the natural bone’s strength. Significant loads may cause implants to fail.
The user’s glove or skin may be pinched or torn by the sharp edges or moving joints of some instruments, screws, and cut plates.
Be sure to get rid of any fragments that weren’t fixed during surgery.
While the surgeon will ultimately decide whether to remove the implant, we advise that fixation devices be taken out as soon as it is safe and practical for the specific patient and after their purpose as a healing aid has been fulfilled. To prevent refracture, proper post-operative management should be performed after pin removal.
Schanz Pin General Adverse Events
There are risks, side effects, and adverse events associated with all major surgical procedures. While there are many possible reactions, the following are some of the most frequent ones: issues related to anesthesia and patient positioning (such as nausea, vomiting, dental injuries, neurological impairments, etc.), thrombosis, embolism, infection, damage to nerve and/or tooth roots or other critical structures, such as blood vessels, excessive bleeding, damage to soft tissues, including swelling, abnormal scar formation, functional impairment of the musculoskeletal system, and pain.
| Schanz Screw (Schanz Pin) Self Tapping |
|---|